The cell wall of prokaryotes : peptidoglycan and related molecules
원핵생물에서의 세포벽 : 펩티도글라이칸과 관련된 분자들(Peptidoglycan and related molecules)
Bacteria의 세포는 solutes에 용해될 수 있는 물질이 높은 농도로 구성되어 있다.
이러한 이유에서, E.coli같은 bacterial cell의 2 ,atmospheres정도의 압력이 생기는데, 이것은 tire의 압력과 같다.
이러한 압력에 의해서도 cell이 터지지 않는 이유는 bacteria가 cell walls를 가지고 있기 때문인데, Cell wall은 세포의 모양 변화를 막아주고, 세포가 단단할 수 있는 기능을 준다.
우리는 Bacteria에서 gram positive와 gram negative라고 불리는 두 주요 group의 cell wall을 찾아볼 수 있다.
Gram positive와 gram negative 사이의 차이점을 관찰하는 방법으로는 gram stain이 있는데, 그런, cell wall structure의 차이는 gram-staining reaction에 핵심이 있다.
Gram negative cell wall은 여러 개의 층으로 구성된, 완전히 complex된 구조로 되어 있고, 이에 대조적으로, Gram-positive cell wall은 molecule의 single type의 1차 구조로 형성되어 있고 매우 얇다.
Cell wall에 대한 초점은 prokaryotes인 bacteria와 archaea의 cell walls의 polysaccharide component에 맞추고 있다.
Peptidoglycan
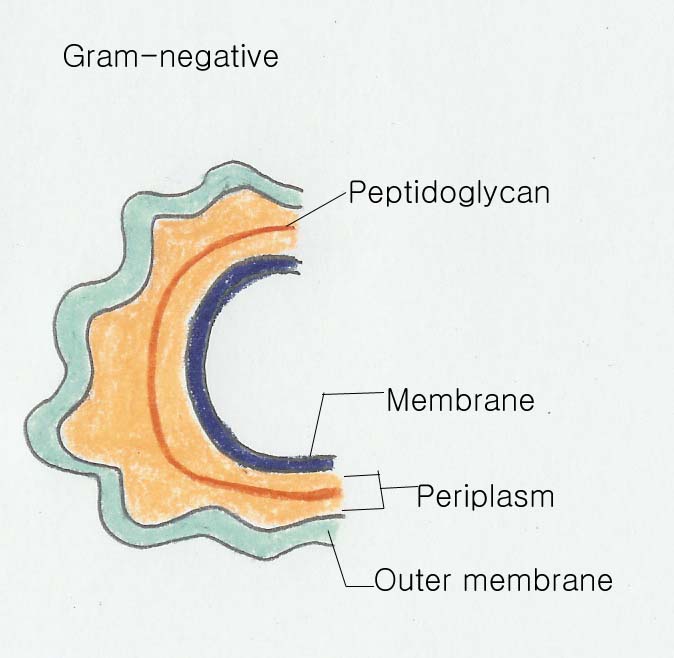
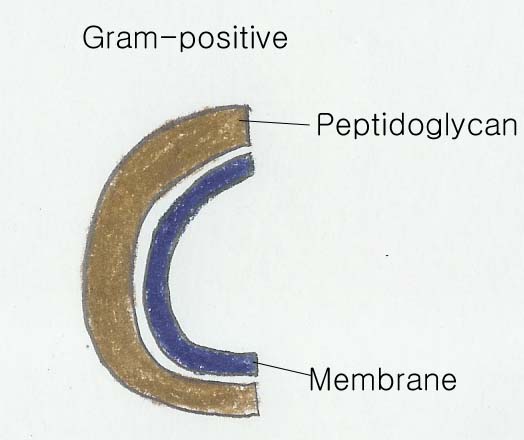
Bacteria의 cell walls는 단단한 층으로 구성되어 있는데, 세포벽의 길이를 위하여 1차적으로 필요한 것이다.
Gram negative bacteria에서 추가되는 층은 이 단단한 층의 바깥쪽에서 나타난다.
Gram negative와 gram positive bacteria의 단단한 층은 화학적 구조가 매우 유사하다. Peptidoglycan이라고 불리는, 이 polysaccharide는 두 개의 sugar로 나뉘어질 수 있는데, 이 두 개의 molecules는 N-acetylglucosamine과 N-acetylmuramic acid로 나뉘어질 수 있고, L-alanine, D-alanine, D-glutamic acid와 같은 특이한 amino acids, 그리고 lysine 또는 diaminopimelic aced(DAP) 둘 중 하나를 포함하게 된다.
이 구성 요소들은 glycan tetrapeptide라는 반복되는 구조의 연결로 구성되어 있다.
Peptidoglycan의 기본적인 구조는 cell 주변에 peptidoglycan이 다른 하나와 결합해서 뉘워있는 형태로 구별되서 구성되어 있다. Tetrapeptide cross-links로부터 연결된 sheet form인 glycan chain은 amino acid로 구성되어 있다. Glycan strands의 sugars로 연결된 glycosidic bonds는 매우 강하다. 그러나 이 chains는 혼자 있으면 모든 방향의 단단함을 가질 수 없게 된다.
Peptidogylcan structures의 full strength는 아미노산에 의해서 cross-linked 되어 있다. 이 cross-linking은 서로 다른 bacteria에서 다른 길이로 나타나고, cross-linking이 많이 되면 될수록 더 단단해지고 견고해진다. Gram-negative bacteria에서, cross-linkage는 terminal D-alanine의 carboxyl group에서 diaminopimelic acid의 amino group의 peptide linkage에 의해서 일어난다.
Gram positive bacteria에서, cross-linkage는 peptide interbridge의 방법에 의해서 일어나는데, amino acid의 종류와 수는 organisms에 따라서 매우 다양하게 나타난다. 예를 들어, Staphylococcus aureus, Gram positive bacterium중 가장 잘 연구되어 있는 이것을, 5개의 glycine molecule이 interbridge로 peptide를 구성하고 있다.
Gram-positive bacteria에서 cell wall의 90% 이상은 peptidoglycan으로 구성되어 있고, teichoic acid라고 불리는 다른 molecule은 매우 적은 양만을 찾아볼 수 있다. 그리고 어떤 bacteria에서는 cell을 둘러싸고 있는 peptidoglycan의 single layer로만 구성된 것도 있다. 많은 bacteria, 특히 Gram-positive bacteria는 일반적으로 peptidoglycan의 sheets가 다른 것들과 함께 한 무더기를 만들어 낸다.
Gram-negative bacteria의 cell wall은 오직 10% 만이 peptidoglycan으로 구성되어 있다. 그러나 Gram-positive와 Gram-negative 둘의 세포의 형태는 peptidoglycan chains의 길이에 의해서 그리고 chains의 cross-linking의 길이에 의해서 결정이 된다.
Diversity in Peptidoglycan
Peptidoglycan은 특별한 bacteria에서만 나타난다. Sugar인 N-acetylmuramic acid와 amino acid인 diamino pimelic acid는 Archaea또는 Eukarya의 cell wall에서 찾을 수 있다. 그러나, 모든 bacteria가 그들의 peptidoglycan에 DAP를 가지고 있는 것은 아니다.
모든 Gram-negative bacteria에서 peptidoglycan이 나타나지만 그러나 대부분의 Gram positive cocci는 DAP의 lysine이 대신한다. 그리고 Gram positive bacteria는 다른 amino acid를 갖는다. 다른 흔히 나타나지 않는 peptidogylcan의 두 가지 amino acid가 나타나는데 이것은 D- configuration과 D-alanin 그리고 D-glutamic acid이다.
100가지 이상의 서로 다른 peptidoglycan types가 알려져 있고, 다양한 interbridge를 형성하고 있다.
Glycan portion의 각각의 다른 peptidoglycan structure는 단일 형태이고, sugar인 N-acetylglucosamine과 N-acetylmuramic acid가 나타난다. 이 sugars는 β-1,4 linkage로 연결이 되어 있다.
반복되는 unit의 tetrapeptide는 오직 한 amino acid의 주요 다양성을 보여주고, lysine-diamino pimelic acid가 교대로 나타난다. 그러나, position 2에서 D-glutamic acid가 어떤 organisms에서 hydroxylated로 결합하고, 다른 어떤 것에서는 1,3 position의 amino acid에서 substitutions가 일어난다.
Tetrapeptide에서 나타나는 amino acids의 어떤 것은 interbridge에서 일어날 수 있다. 그러나 추가로, glycine, theonine, serine, 그리고 aspartic acid 같은 amino acid는 interbridge에서 찾을 수 있다. 그러나, branch를 이루고 있는 amino acids, aromatic amino acids, sulfur-containing amino acids, histidine, arginine, 그리고 proline은 interbridge에서 찾을 수 없다.
그러므로, peptidoglycan의 peptide chemisty, peptidoglycan의 backbone - glucosamine과 muramic acid의 반복이 교대로 일어나는 - 은 bacteria의 모든 종에서 동일하게 나타난다.
Teichoic acids is a summary of the Gram-positive wall
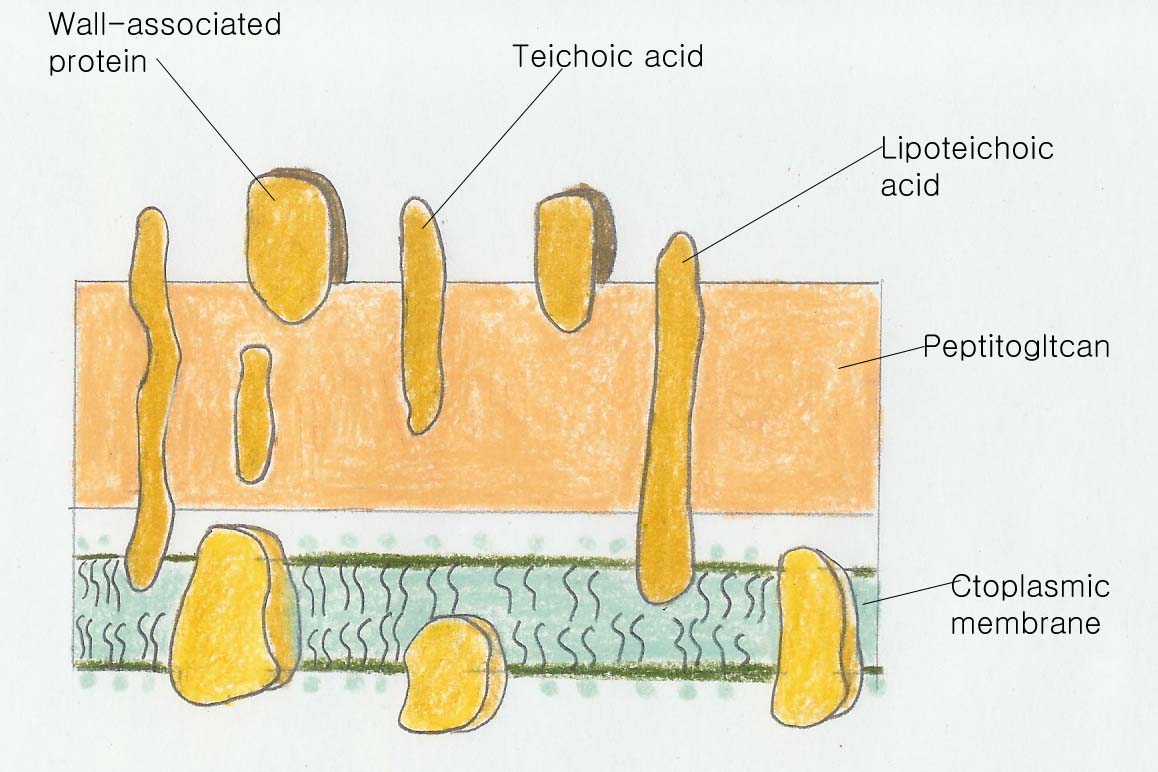
많은 Gram-positive bacteria는 그들의 세포벽에 teichoic acids라고 불리는 acidic substances를 가지고 있다. 모든 cell의 wall과 membrane 또는 capsular polymers를 구성하는 glycerophosphate 또는 ribitol phosphate residues가 teichoic acid에 포함된다. 이 polyalcohols는 phosphate seters에 의해서 연결되어 있고, 대게 다른 sugars와 D-alanine이 attached 되어 있다. 왜냐하면 그들은 negative charge를 띄고 있고, teichoic acids는 cell 표면의 negative charge를 위해 필요한 부분이다.
Teichoic acids는 또한 Ca와 Mg같은 2가 양이온을 binding 할 수 있는 기능을 가지고 있다.
이들 중 일부는 cell내로 transported되어진다. 확실한 teichoic acids는 membrane lipids에 covalently bound하고 있고, 이러한 이유에서 이들은 lipoteichoic acids라고 불린다.
Cells with no walls
Peptidoglycan -bacteria의 species의 특징정인 molecule- 은 확실한 작용물질로부터 파괴될 수 있다.
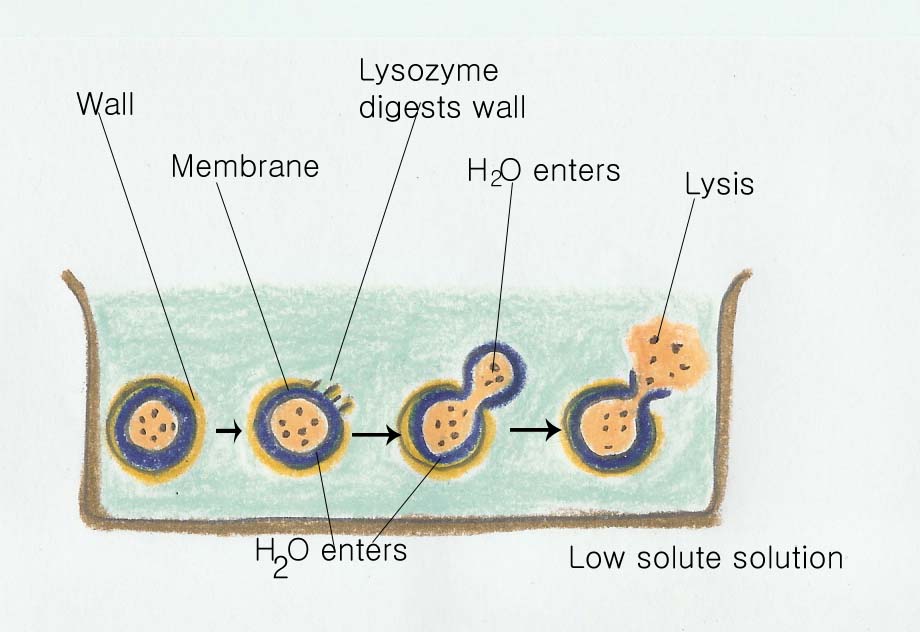
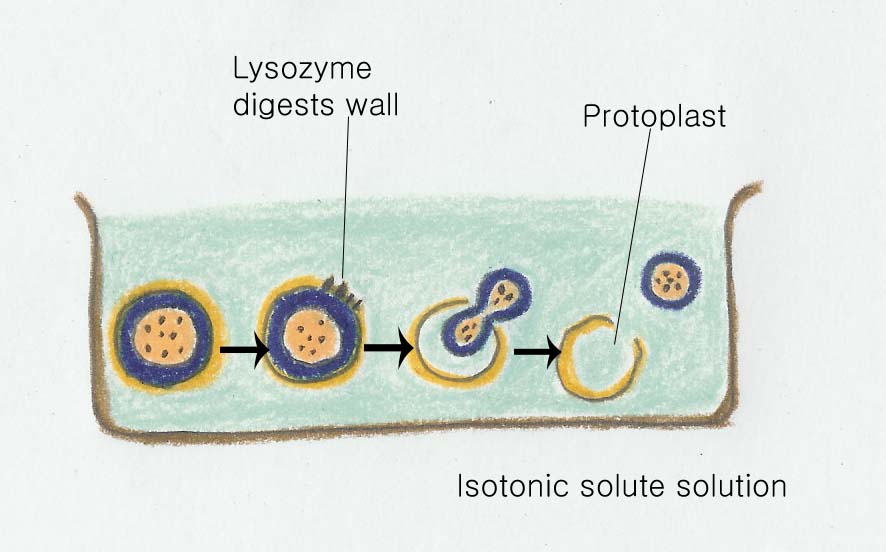
Enzyme인 lysozyme같은 protein은 peptidogylcan의 N-acetylglucosamine과 N-acetylmuramic acid 사이의 β-1,4-glycosidic bonds를 깨주는 역할을 한다. 물이 cell안으로 들어가면, cell이 부풀어 오르고 결과적으로 cell이 터지게 되는데 이러한 과정을 lysis라고 한다. Lysozyme은 tears, saliva, 외 다른 몸의 유동체를 가지고 있는 animal 내에서 찾을 수 있고, bacteria에 의해서 감염이 되면 그 기능이 나타난다.
만약, solute가 세포 내로 들어가지 않으면, sucrose 같은 것을 cell 현탁액에 첨가해 주면, cell 바깥의 solute농도가 내부와 같게 된다(이러한 condition을 isotonic이라고 한다). 이러한 상태 아래에서 lysozyme은 여전히 peptidoglycan을 끊지만, 물이 cell 안으로 들어가지 못해서 cell lysis가 일어나지 않게 된다. 대신에 protoplast(bacteria가 cell wall을 가지고 있지 않은 상태)를 찾을 수 있다. 만약, sucrose에 의해서 안정화된 protoplast가 물 안으로 들어가게 되면 cell lysis가 다시 일어나게 된다. Spheroplast는 protoplast와 함께 사용되는 동의어이지만, 두 단어는 유사하면서도 다른 의미를 가지고 있다.
Protoplasts는 남겨진 cell wall material에서 세포가 자유로워진 것을 이야기하는데 비해 spheroplasts는 wall meterial의 구성 부분이 membrane으로 둘러 쌓인 structrue에 다른 방법으로 attached 되어 있는 것을 이야기한다. 비록, 대부분의 prokaryotes가 그들의 cell wall이 없이 ,자연 상태에서 살아갈 수는 없지만, 일부는 살아갈 수 있다.
Mycoplasmas를 포함하는, infectious diseases의 원인이 되는 group과 thermoplasma group, Archaea는 자연 상태에서 cell wall이 결여되어 있는 상태이다. 이 prokaryotes는 free-living protoplasts이고 cell wall 없이 살아갈 수 있는데 animal body 같은 혀의 membrane 또는 삼투압이 형성될 수 있는 환경에서 살아갈 수 있기 때문이다. Mycoplasmas는 그들의 cell membranes에 sterols를 가지고 있는데 이것의 구조는 단단하고 세기가 강하다.
Pseudopeptidoglycan, S-layers and other cell wall of Archaea
Archaea의 어떤 species는 peptidoglycan과 매우 유사한 polysaccharide로 cell wall이 구성되어 있다. 이러한 materials를 pseudopeptidoglycan이라고 한다. Pseudopeptidoglycan의 backbone은 N-acetylglucosamine과 N-acetyltalosaminuronic acid의 반복으로 구성되어 있다(Peptidoglycan의 N-acetylmuramic acid와 나중에 replaces)
Glycosidic bonds의 peptidoglycan으로부터 나온 β-1,3-bonds로 glycosidic bonds를 형성한다. 다른 Archaea의 세포벽은 peptidoglycan과 pseudopeptidoglycan, 그리고 polysaccharide, glycoprotein 또는 protein의 구성요소로 잘려 있다. 예를 들어, Methanosarcina species는 glucose, glucoronic acid, galactosamine 그리고 acetate 같은 구성물질로 얇은 polysaccharide를 구성하고 있다.
Halococcus 같은 Extremely haophilic(Salt-loving) Archaea는 Methanosarcina의 cell wall과 유사하지만, 거기에 Sulfate residues가 더 첨가되어 있다.
Archaea 사이에서 가장 일반적으로 나타나는 cell wall type은 paracrystalline surface layer(S-layer)이다. Protein 또는 glycoprotein의 구성요소인 S-layer는 일반적으로 hexagonal symmetry이다. S-layers는 Archaea의 모든 group의 species, extreme halophiles, methanogens, hyper thermophiles 사이에서 찾을 수 있다.
Bacteria의 일반적 species는 또한 그들의 outer surface 에서 S-layer를 찾을 수 있다.
Archaea의 species에서 우리는 또한 다양한 cell wall chemistries를 찾을 수 있는데, polysaccharide component를 종합적으로 lacking 한 wall 의 peptidoglycan과 공통점이 있는 molecules로 부터 다양성을 가진다.
그러나 매우 적은 예로, 모든 Archaea는 약간의 sort로 cell wall이 구성되어 있고, bacteria에서 Archaeal cell wall 기능을 나타내는 osmotic lysis와 세포 모양을 결정할 수 있는 기능을 가지고 있다. 게다가, 그들의 cell wall 의 peptidoglycan이 깨져있기 때문에, 모든 Archaea는 일반적으로 lysozyme과 penicillin의 활성에 저항성을 가지고 있다.
The outer membrane of Gram negative bacteria
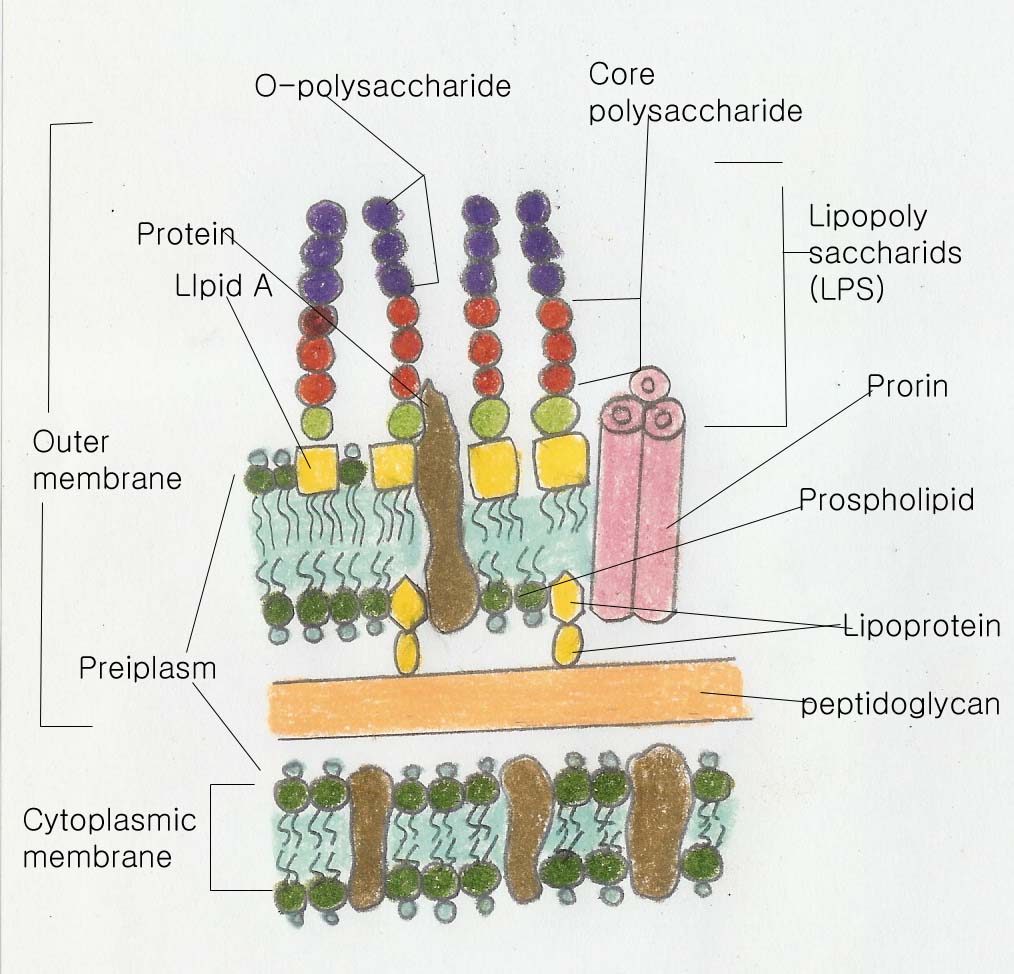
Peptidoglycan에 더해서, Gram-negative bacteria는 wall layer가 더해져서 구성되어 있는데 이것을 outer membrane이라고 한다. 이 layer는 두 번째 lipid bilayer 이지만 cytoplasmic membrane의 phospholipid와 protein 혼자서 구성되어지지는 않는다.
Outer membrane은 또한 polysaccharide로 구성되어 있다. Lipid와 polysaccharide는 lipopolysaccharide complex form으로 outer membrane에서 연결되어 있다. 이러한 이유에서, outer membrane은 종종 lipopolysaccharide layer 또는 LPS라고 부른다.
Chemistry of LPS
비록 complex이지만, 일반적 Bacterial로부터 LPS의 화학적 구성 요소는 아직 밝혀지지 않았다.
LPS의 polysaccharide portion은 두 개의 components로 구성이 되는데, core polysaccharide와 O-polysaccharide이다. Salmonella species에서 LPS가 가장 잘 연구가 되어 있는데, ketodeoxyoctonate(KDO)의 구성성분인 core polysaccharide, 7개의 탄소로 구성된 sugar(heptoses), glucose, galactose, 그리고 N-acetylglucosamine 등이 있다. Core의 연결체는 O-specific polysaccharide인데, 이것은 galactose, glucose, rhamnose 그리고 mannose(모두 hexose)로 구성되어 있고, 하나 또는 더 많은 일반적이지 않는 abquose, colitose, paratose 또는 tyvelose같은 dideoxy sugars로 구성되어 있다.
이 sugars는 4개 또는 5개의 membered sequences로 연결되어 있고, 종종 branch를 형성한다. Sequences가 반복될 때, 긴 O-polysaccharide가 형성된다.
Lipopolysaccharide의 lipid portion은, lipid A에 속하는, glycerol lipid는 아니지만, N-acetylglucosamine phosphate의 desaccharide로 구성된 amine ester linkage로부터 연결된 fatty acid로 되어 있다. Disaccharide는 KDO를 통해서 core polysaccharide와 attached 되어 있다.
Fatty acids는 일반적으로 caproic, lauric, myristic, palmitic 그리고 stearic acids등을 포함하는 lipid A에서 찾을 수 있다.
다른 membrane에서 LPS는 membrane의 바깥쪽 소엽 모양의 구조의 protein과 함께 연결되어 있다. A lipoprptein complex는 gram negative bacteria의 number의 LPS의 내부 소엽 모양의 그것과 찾아진다.
Lipoprotein의 기능은 바깥쪽 막과 peptidoglycan사이에 끼어들어가 있다.
마지막으로, outer membrane의 바깥쪽 소엽 모양의 부분은, LPS가 phospholipids와 replaced, 이것은 오직 내부 소엽 모양 부분에서 찾을 수 있다. 그러므로, 바깥쪽 membrane이 lipid bilayer라고 생각될 수도 있지만, 이것의 구조는 cytoplasmic membrane과는 구별되는 구조를 가지고 있다.