Antibidy (항쳬)
Antibody (항체, 이하 Ab)는 높은 친화력으로 주어진 Antigen (항원, 이하 Ag)에 붙을 수 있는 유용한 반응물
- Ag의 정확한 subcellular (세포 이하의) 위치를 파악하고, 정확한 농도로 반응
- Ag과 작용하는 다른 molecule까지 포함
- Ab 생산 ; 특정 Ag을 실험 동물에게 주입, serum sample을 얻음
Serum은 서로 다른 epitope상의 Ag과 binding하는 Ab 집단을 말함
- epitope : Ag상에서 Ab가 binding하는 부위
- 특정의 epitope을 인식하는 Ab의 개별 type은 plasma cell (혈장 세포)의 서로 다른 clone에 의해 생산됨 -> 각각의 plasma cell은 오직 하나의 epitope에만 binding하는 Ab를 분비
- Serum 내의 Ab 집단은 많은 종류의 서로 다른 Ab-producing plasma cell에 의해 생산됨
Ag -> mouse -> 1) serum 분리 -> polyclonal Ab (immunochemical technique에 가장 많이 쓰임)
2) spleen cell 분리 -> plasma cell + myeloma cell fusion -> hybridoma -> select -> clone들로부터 monoclonal Ab를 얻음 (tissue culture supernatant로 사용됨)
* Commonly used sources of antibodies *
| Ab source | Ab type | Total Ab concentration | Specific Ab concentration | Contaminating |
| Serum | polyclonal | 10 mg/ml | normally less than 0.5 mg/ml | other serum Abs |
Tissue culturesupernatantwith 10% FBS |
monoclonal | 1 mg/ml | 0.05 mg/ml | Calf Abs |
| Ascites (복수) | monoclonal | 1~10 mg/ml | 0.9~9 mg.ml | Mouse Abs |
Ab는 1) Ag binding site와 2) cell-binding region으로 구성된다
- secreted glycoprotein
- Y자 형태의 characteristic unit을 한 개 또는 그 이상 가진다
- IgG : 오직 하나의 Y unit, serum 내에 가장 많이 존재하는 immunoglobulin
* IgG : 3개의 protein region을 가짐 (protease papain으로 3 부분이 잘림)
1) Ag binding region
2) Fab domain (fragment having the Ag binding site) : 2개의 Ag binding domain의 lateral, rotational movement에 관여 (다른 Ag과 binding할 수 있도록)
3) Fc domain (fragment that crystalizes) : immune response에 중요 ( ex. macrophage와의 interaction, activation of complement 등)
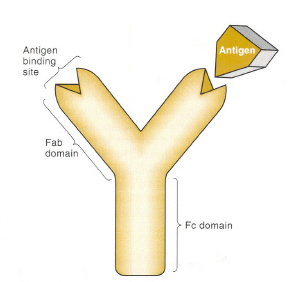
Antibody Domains
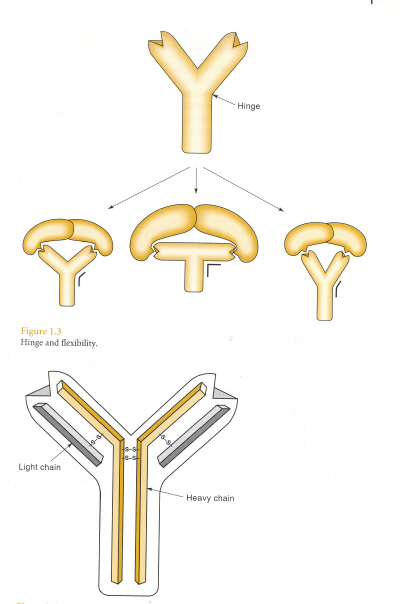
IgG protein은 2개의 heavy chain polypeptide (Hc, 55000 Da) 와 2개의 light chain polypeptide (Lc, 25000Da) 로 구성
1개의 Lc -> Hc의 amino terminal과 interaction -> Ag binding site
2개의 Hc의 carboxyl terminal region은 서로 fold -> Fc domain
4개의 Hc, Lc -> covalent disulfide bridge & noncovalent bond로 결함
Ab의 종류 (Hc의 Fc fragment의 유형에 따라)
IgG, IgM, IgA, IgE, IgD
* Class of antibodies *
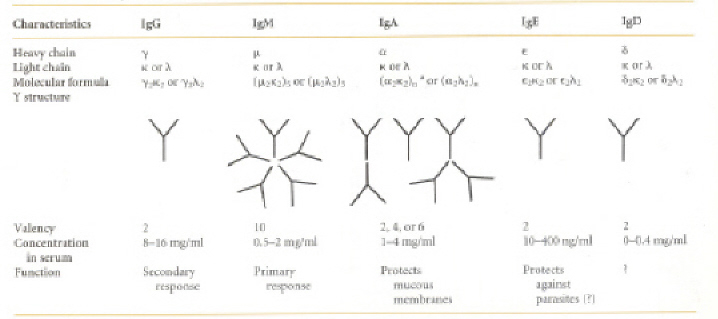 -
-
- Hc은 5종류, 그러나 Lc는 오직 2개
- 하나의 Lc는 항상 하나의 Hc와 association
-> Lc의 갯수 = Hc의 갯수
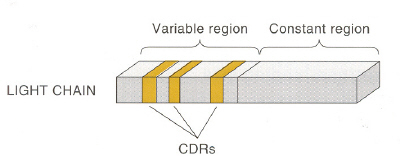
Lc의 primary amino acid sequence의 비교는 constant, variable region을 나타내 준다
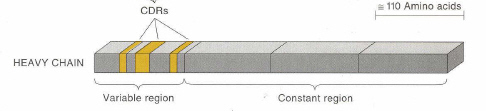
- Lc : 220 a.a 길이, 2region으로 나뉨 (약 110 a.a 길이로)
* Coding region *
| mouse | human | |
| k light chain | chromosome 6 | chromosome 2 |
| λ light chain | chromosome 16 | chromosome 22 |
Hc의 sequence 비교는 역시 variable, constant region을 밝혀 준다
- IgG의 Hc은 440 a.a 길이
- 역시 variable (amino term), constant (carboxyl term)으로 나뉜다
- 그러나, 하나의 variable region을 가지고 3개의 constant region을 가진다. (lihgt, heavy chain 모두 1개의 region은 110 a.a 길이이다)
- IgM의 u chain은 1개의 variable, 4개의 constant region을 가지기도 한다.
- IgG Hc은 4개의 r chain subclass를 가지기도 한다
ex) mouse에서 IgG는 IgG1, IgG2a, IgG2b, IgG3를 가진다
* Coding region *
| heavy chain | ||
| mouse | chromosome 12 | |
| human | chromosome 14 |
Hc와 Lc의 variable region들이 Ag-binding site 형성한다
- Ag과 결합하는 부위의 5~10 a.a (hypervariable region의) 에서 sequence heterogeity가 생김
-> Lc의 3군데 hypervariable region, Hc의 3군데 hypervariable region에서 대부분의 variability가 발생
-> CDR (complementarity determining region)
다수의 genetic mechanisms이 Ag binding site에서의 격렬한 diversity를 제공한다
- at animal ;
각각의 Ab가 B cell or progeny plasma cell의 clone으로부터 분비됨
따라서, Ag binding site의 diversity는 수많은, 서로 다른 B cell clone (specofoc한 Ag binding site를 가지는 서로 다른 Ab를 분비하는) 을 생산하는 능력을 측정하는 수단이 된다
- Light, Heavy chain의 variable region에서 heterogeneity를 일으키는 4가지 요인 *
1) 각각의 Ag binding site 부분을 specifying하는 여러 coding segment들의 사용
2) 약간의 정확하지 않은 homologous recombination
- 최종 Ab sequence를 만들기 위한 다양한 coding region들의 재조정 & 임의의 nucleotide를 붙이면서 recombination joint에 붙이면서 novel한 diversity 생성
3) Coding region에서의 mutation 생성
4) 3가지 유형 (CDR)의 change들을 가지고 있는 서로 다른 Hc, Lc의 random한 association
- 보통 animal들은 10의 12개의 서로 다른 Ag-binding domain들을 생산
- 각각의 서로 다른 Ab들은 오직 B cell들의 하나의 clone에 의해 생산되기 때문에, B cell의 분화와 progenitor들은 한정된 focus를 가진 Ab의 생산에 specialize!
- 특정 Ag에 노출되는 동안, Ag의 epitope에 specific한 Ab를 생산하는 B cell들은 plasma membrane에 수송될 목적으로 변형된 Ab, 즉 Ag 수용체에 관여함으로 해서, 선별된다 -> 이렇게 자극을 받은 B cell들은 표면에 있는 Ab들이 Ag에 얼마나 잘 붙는가에 기초하여 증식 (proliferation)을 겪고, 증식 동안 더욱 정제된 Ag-binding site를 이끌어 내는 further variation을 introduce -> Ag 노출의 마지막 단계에서, 높은 Ag-binding 친화력을 가진 Ab들을 만들어낸 cell들은 선별되고, 증식, 다양화를 목적하에 더욱 자극을 받게 된다 -> 더욱 질 좋은 Ab를 생산하게 되는 것임
부가적인 재조합 과정들은 서로 다른 Ab의 class, subclass들을 생산해 낸다
- immune response의 maturation은 Hc의 constant region에서의 recombination을 유발 (variable region, Ag binding site에게는 영향을 끼치지 않는다)
-> 하나의 Hc constant region을 다른 것으로 교체!!
- Rearrangement는 variable region 으로부터 downstream에서 생긴다
ex) Hc의 다양한 r chain gene인 (u, IgM) (a, IgA) (e, IgE) (d, IgD)
-> immunoglobilin class마다 constant region에서의 domain들은 다르게 가진다 -> Hc의 서로 다른 constant region은 immune response 동안 특정의 기능을 하게 되는 것임
Variable domain들은 Ag binding과 specificity를 제공하고, constant domain들은 얼마나 Ab가 function하는지를 결정한다
- constant region은 secondary reagent와의 interaction에 필요한 중요한 site를 제공하기도 한다 *
- constant region은 Ag-binding와 거리가 있기 때문에, Ag-binding와 거리가 있기 때문에, Ag-binding site에서의 Ag-Ab binding의 방해없이 Ab와 작용할 수 있는 site를 제공한다
- protein A와 G가 Ab에 결합하는 부위, 대부분의 secondary Ab의 epitope이 binding할 수 있는 부위가 되는 것임