Difference between revisions of "Biology"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | <p><strong>Biology</strong> (from Greek: βίος, <em>bio</em>, "life"; and λόγος, <em>logos</em>, "knowledge") is the study of life. It contains such topics as classifying the various forms of organisms, how species come into existence, and the interactions they have with each other and with the natural environment. Biology encompasses a broad spectrum of academic fields that are often viewed as independent disciplines. However, together they address phenomena related to living organisms (biological phenomena) over a wide range of disciplines, many of which, for example, botany, zoology, and medicine are considered ancient fields of study.</p> | + | <p><strong><font size="3">Biology</font></strong> (from Greek: βίος, <em>bio</em>, "life"; and λόγος, <em>logos</em>, "knowledge") is the study of life. <br /> |
| + | Biology is an information science that is close to computer science and mathematics. The early 2000s was at the point where the conventional views of molecular biology changed rapidly with new views. One of them is the transition from the object-oriented understanding of biology to an interaction-oriented understanding. <br /> | ||
| + | Many scientists have predicted the reverse of reductionism in biology in the past, and such interaction-based molecular research is the starting point of a holistic way. <br /> | ||
| + | The most appropriate and general name of such a non-reductionist methodology of doing biology is perhaps omics. We now have enough individual objects in biology to look at the architecture of the biological information object networks. [[Network biology]] and [[systems biology]] are sub branches of biology where [[omics]] paradigm is applied.<br /> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | It contains such topics as classifying the various forms of organisms, how species come into existence, and the interactions they have with each other and with the natural environment. Biology encompasses a broad spectrum of academic fields that are often viewed as independent disciplines. However, together they address phenomena related to living organisms (biological phenomena) over a wide range of disciplines, many of which, for example, botany, zoology, and medicine are considered ancient fields of study.</p> | ||
<p>Biology as a unified science was first developed in the nineteenth century, as scientists discovered that all living things shared certain fundamental characteristics and were best studied as a whole. Over a million papers are published annually in a wide array of biology and medicine journals,<sup class="reference" id="_ref-0">[1]</sup> and biology is a standard subject of instruction at schools and universities around the world.</p> | <p>Biology as a unified science was first developed in the nineteenth century, as scientists discovered that all living things shared certain fundamental characteristics and were best studied as a whole. Over a million papers are published annually in a wide array of biology and medicine journals,<sup class="reference" id="_ref-0">[1]</sup> and biology is a standard subject of instruction at schools and universities around the world.</p> | ||
<p>As such a vast field, biology is divided into a number of disciplines. The old divisions by type of organism remains with subjects such as botany encompassing the study of plants, zoology with the study of animals, and microbiology as the study of microorganisms. The field may also be divided based on the scale at which it is studied: biochemistry examines the fundamental chemistry of life; cellular biology examines the basic building block of all life, the cell; Physiology examines the mechanical and physical functions of an organism; and ecology examines how various organisms interrelate. Applied fields of biology such as medicine are more complex and involve many specialized sub-disciplines.</p> | <p>As such a vast field, biology is divided into a number of disciplines. The old divisions by type of organism remains with subjects such as botany encompassing the study of plants, zoology with the study of animals, and microbiology as the study of microorganisms. The field may also be divided based on the scale at which it is studied: biochemistry examines the fundamental chemistry of life; cellular biology examines the basic building block of all life, the cell; Physiology examines the mechanical and physical functions of an organism; and ecology examines how various organisms interrelate. Applied fields of biology such as medicine are more complex and involve many specialized sub-disciplines.</p> | ||
Revision as of 00:06, 31 May 2007
Biology (from Greek: βίος, bio, "life"; and λόγος, logos, "knowledge") is the study of life.
Biology is an information science that is close to computer science and mathematics. The early 2000s was at the point where the conventional views of molecular biology changed rapidly with new views. One of them is the transition from the object-oriented understanding of biology to an interaction-oriented understanding.
Many scientists have predicted the reverse of reductionism in biology in the past, and such interaction-based molecular research is the starting point of a holistic way.
The most appropriate and general name of such a non-reductionist methodology of doing biology is perhaps omics. We now have enough individual objects in biology to look at the architecture of the biological information object networks. Network biology and systems biology are sub branches of biology where omics paradigm is applied.
It contains such topics as classifying the various forms of organisms, how species come into existence, and the interactions they have with each other and with the natural environment. Biology encompasses a broad spectrum of academic fields that are often viewed as independent disciplines. However, together they address phenomena related to living organisms (biological phenomena) over a wide range of disciplines, many of which, for example, botany, zoology, and medicine are considered ancient fields of study.
Biology as a unified science was first developed in the nineteenth century, as scientists discovered that all living things shared certain fundamental characteristics and were best studied as a whole. Over a million papers are published annually in a wide array of biology and medicine journals,[1] and biology is a standard subject of instruction at schools and universities around the world.
As such a vast field, biology is divided into a number of disciplines. The old divisions by type of organism remains with subjects such as botany encompassing the study of plants, zoology with the study of animals, and microbiology as the study of microorganisms. The field may also be divided based on the scale at which it is studied: biochemistry examines the fundamental chemistry of life; cellular biology examines the basic building block of all life, the cell; Physiology examines the mechanical and physical functions of an organism; and ecology examines how various organisms interrelate. Applied fields of biology such as medicine are more complex and involve many specialized sub-disciplines.
Contents
Foundations of modern biology
Biology is a branch of science that characterizes and investigates living organisms utilizing the scientific method. There are four broad unifying principles of biology:
- Cell theory. All living organisms are composed of at least one cell and the cell is the basic unit of function in all organisms. In addition, the chemical composition of all cells in all organisms is similar, and emerge from preexisting cells through cell division or mitosis.
- Evolution. Through natural selection or genetic drift, a population's inherited traits change from generation to generation.
- Gene theory. A living organism's traits are encoded into DNA that is the fundamental component of genes. In addition, genes transfer an organism's traits from one generation to the next.
- Homeostasis. The physiological processes that allow an organism to maintain its internal environment notwithstanding its external environment.
Cell Theory
Cell theory states that all living things are composed of one or more cells as well as the secreted products of those cells, for example, plasma, extracellular matrix, and bone. These cells arise from other cells through cell division, and that in multicellular organisms, every cell in the organism's body has been produced from the single cell in a fertilized egg.
Evolution
A central organizing concept in biology is that all life has a common origin and has changed and developed through the process of the theory of evolution (see Common descent). This has led to the striking similarity of units and processes discussed in the previous section. Charles Darwin established evolution as a viable theory by articulating its driving force, natural selection (Alfred Russel Wallace is recognized as the co-discoverer of this concept). Darwin theorized that species and breeds developed through the processes of natural selection as well as by artificial selection or selective breeding.Genetic drift was embraced as an additional mechanism of evolutionary development in the modern synthesis of the theory.
The evolutionary history of a species— which describes the characteristics of the various species from which it descended— together with its genealogical relationship to every other species is called its phylogeny. Widely varied approaches to biology generate information about phylogeny. These include the comparisons of DNA sequences conducted within molecular biology or genomics, and comparisons of fossils or other records of ancient organisms in paleontology. Biologists organize and analyze evolutionary relationships through various methods, including phylogenetics, phenetics, and cladistics (The major events in the evolution of life, as biologists currently understand them, are summarized on this evolutionary timeline).
Ever since its articulation by Darwin and Wallace, the theory of evolution by natural selection has come under attack by people who disagree with scientific findings or interpretations regarding the origins and diversity of life, generally favoring instead religious explanations. See Creation-evolution controversy for more information.
Up into the 19th century, it was commonly believed that life forms could appear spontaneously under certain conditions (see abiogenesis). This misconception was challenged by William Harvey's diction that "all life [is] from [an] egg" (from the Latin "Omne vivum ex ovo"), a foundational concept of modern biology. It simply means that there is an unbroken continuity of life from its initial origin to the present time.
A group of organisms shares a common descent if they share a common ancestor. All organisms on the Earth have been and are descended from a common ancestor or an ancestral gene pool. This last universal common ancestor of all organisms is believed to have appeared about 3.5 billion years ago. Biologists generally regard the universality of the genetic code as definitive evidence in favor of the theory of universal common descent (UCD) for all bacteria, archaea, and eukaryotes (see: origin of life).
Gene theory
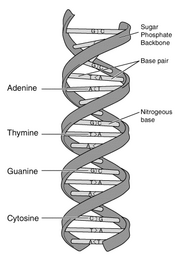
While organisms may vary immensely in appearance, habitat, and behaviour it is a central principle of biology that all life shares certain universal fundamentals. A key feature is reproduction or replication. The entity being replicated, the replicator, in the past was considered to be the organism during the time of Darwin, but since the 1970s increasingly reduced to the scale of molecules.[2] All known life has a carbon-based biochemistry, carbon is the fundamental building block of the molecules that make up all known living things. Similarly water is the basic solvent for all known living organisms. While all these things are true of all organisms observed on Earth, in theory alternative forms of life could exist and some scientists do look at alternative biochemistry.
All terrestrial organisms use DNA and RNA-based genetic mechanisms to hold genetic information. Another universal principle is that all observed organisms with the exception of viruses are made of cells. Similarly, all organisms share common developmental processes.
Homeostasis
Homeostasis is the ability of an open system to regulate its internal environment to maintain a stable condition by means of multiple dynamic equilibrium adjustments controlled by interrelated regulation mechanisms. All living organisms, whether unicellular or multicellular, exhibit homeostasis. Homeostasis manifests itself at the cellular level through the maintenance of a stable internal acidity (pH); at the organismic level, warm-blooded animals maintain a constant internal body temperature; and at the level of the ecosystem, as when atmospheric carbon dioxide levels rise and plants are theoretically able to grow healthier and remove more of the gas from the atmosphere. Tissues and organs can also maintain homeostasis.
Scope
Biology has become such a vast research enterprise that it is not generally regarded as a single discipline, but a number do assist in understanding the genetic variation of a population; and physiology borrows extensively from cell biology in describing the function of organ systems. Ethology and comparative psychology extend biology to the analysis of animal behavior and mental characteristics, whilst Evolutionary psychology proposes that the field of psychology, including in regard to humans, is a branch of biology.
Common descent
Up into the 19th century, it was believed that life forms were being continuously created under certain conditions (see spontaneous generation). This misconception was challenged by William Harvey's diction that "all life [is] from [an] egg" (from the Latin "Omne vivum ex ovo"), a foundational concept of modern biology. It simply means that there is an unbroken continuity of life from its initial origin to the present time.
A group of organisms shares a common descent if they share a common ancestor. All organisms on the Earth have been and are descended from a common ancestor or an ancestral gene pool. This last universal common ancestor of all organisms is believed to have appeared about 3.5 billion years ago. Biologists generally regard the universality of the genetic code as definitive evidence in favor of the theory of universal common descent (UCD) for all bacteria, archaea, and eukaryotes (see: origin of life).
Structure of life
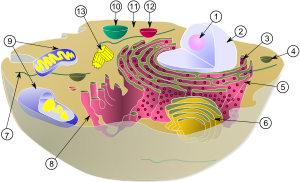
Molecular biology is the study of biology at a molecular level. This field overlaps with other areas of biology, particularly with genetics and biochemistry. Molecular biology chiefly concerns itself with understanding the interactions between the various systems of a cell, including the interrelationship of DNA, RNA, and protein synthesis and learning how these interactions are regulated.
Cell biology studies the physiological properties of cells, as well as their behaviors, interactions, and environment. This is done both on a microscopic and molecular level. Cell biology researches both single-celled organisms like bacteria and specialized cells in multicellular organisms like humans.
Understanding cell composition and how they function is fundamental to all of the biological sciences. Appreciating the similarities and differences between cell types is particularly important in the fields of cell and molecular biology. These fundamental similarities and differences provide a unifying theme, allowing the principles learned from studying one cell type to be extrapolated and generalized to other cell types.
Genetics is the science of genes, heredity, and the variation of organisms. Genes encode the information necessary for synthesizing proteins, which in turn play a large role in influencing (though, in many instances, not completely determining) the final phenotype of the organism. In modern research, genetics provides important tools in the investigation of the function of a particular gene, or the analysis of genetic interactions. Within organisms, genetic information generally is carried in chromosomes, where it is represented in the chemical structure of particular DNA molecules.
Developmental biology studies the process by which organisms grow and develop. Originating in embryology, modern developmental biology studies the genetic control of cell growth, differentiation, and "morphogenesis," which is the process that gives rise to tissues, organs, and anatomy. Model organisms for developmental biology include the round worm Caenorhabditis elegans, the fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster, the zebrafish Brachydanio rerio, the mouse Mus musculus, and the weed Arabidopsis thaliana.
Physiology of organisms
Physiology studies the mechanical, physical, and biochemical processes of living organisms by attempting to understand how all of the structures function as a whole. The theme of "structure to function" is central to biology. Physiological studies have traditionally been divided into plant physiology and animal physiology, but the principles of physiology are universal, no matter what particular organism is being studied. For example, what is learned about the physiology of yeast cells can also apply to human cells. The field of animal physiology extends the tools and methods of human physiology to non-human species. Plant physiology also borrows techniques from both fields.
Anatomy is an important branch of physiology and considers how organ systems in animals, such as the nervous, immune, endocrine, respiratory, and circulatory systems, function and interact. The study of these systems is shared with medically oriented disciplines such as neurology and immunology.
Diversity and evolution of organisms

Main articles: Evolutionary biology, Biodiversity, Botany, Zoology is concerned with the origin and descent of species, as well as their change over time, and includes scientists from many taxonomically-oriented disciplines. For example, it generally involves scientists who have special training in particular organisms such as mammalogy, ornithology, or herpetology, but use those organisms as systems to answer general questions about evolution. Evolutionary biology is mainly based on paleontology, which uses the fossil record to answer questions about the mode and tempo of evolution, as well as the developments in areas such as population genetics and evolutionary theory. In the 1990s, developmental biology re-entered evolutionary biology from its initial exclusion from the modern synthesis through the study of evolutionary developmental biology. Related fields which are often considered part of evolutionary biology are phylogenetics, systematics, and taxonomy.
The two major traditional taxonomically-oriented disciplines are botany and zoology. Botany is the scientific study of plants. Botany covers a wide range of scientific disciplines that study the growth, reproduction, metabolism, development, diseases, and evolution of plant life. Zoology involves the study of animals, including the study of their physiology within the fields of anatomy and embryology. The common genetic and developmental mechanisms of animals and plants is studied in molecular biology, molecular genetics, and developmental biology. The ecology of animals is covered under behavioral ecology and other fields.
Taxonomy

Classification is the province of the disciplines of systematics and taxonomy. Taxonomy places organisms in groups called taxa, while systematics seeks to define their relationships with each other. This classification technique has evolved to reflect advances in cladistics and genetics, shifting the focus from physical similarities and shared characteristics to phylogenetics.
Traditionally, living things have been divided into five kingdoms:
- Monera -- Protista -- Fungi -- Plantae -- Animalia
However, many scientists now consider this five-kingdom system to be outdated. Modern alternative classification systems generally begin with the three-domain system:[3]
- Archaea (originally Archaebacteria) -- Bacteria (originally Eubacteria) -- Eukaryota
These domains reflect whether the cells have nuclei or not, as well as differences in the cell exteriors.
Further, each kingdom is broken down continuously until each species is separately classified. The order is:
- Kingdom
- Phylum
- Class
- Order
- Family
- Genus
- Species
The scientific name of an organism is obtained from its genus and species. For example, humans would be listed as Homo sapiens. Homo would be the genus and sapiens is the species. Whenever writing the scientific name of an organism, it is proper to capitalize the first letter in the genus and put all of the species in lowercase; in addition the entire term would be put in italics or underlined. The term used for classification is called taxonomy.
There is also a series of intracellular parasites that are progressively "less alive" in terms of metabolic activity:
- Viruses -- Viroids -- Prions
The dominant classification system is called Linnaean taxonomy, which includes ranks and binomial nomenclature. How organisms are named is governed by international agreements such as the International Code of Botanical Nomenclature (ICBN), the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature (ICZN), and the International Code of Nomenclature of Bacteria (ICNB). A fourth Draft BioCode was published in 1997 in an attempt to standardize naming in these three areas, but it has yet to be formally adopted. The Virus cInternational Code of Virus Classification and Nomenclature (ICVCN) remains outside the BioCode.
Interactions of organisms
Ecology studies the distribution and abundance of living organisms, and the interactions between organisms and their environment. The environment of an organism includes both its habitat, which can be described as the sum of local abiotic factors such as climate and ecology, as well as the other the organisms that share its habitat. Ecological systems are studied at several different levels, from individuals and populations to ecosystems and the biosphere. As can be surmised, ecology is a science that draws on several disciplines.
Ethology studies animal behavior (particularly of social animals such as primates and canids), and is sometimes considered a branch of zoology. Ethologists have been particularly concerned with the evolution of behavior and the understanding of behavior in terms of the theory of natural selection. In one sense, the first modern ethologist was Charles Darwin, whose book "The Expression of the Emotions in Man and Animals" influenced many ethologists.
Biogeography studies the spatial distribution of organisms on the Earth, focusing on topics like plate tectonics, climate change, dispersal and migration, and cladistics.
Every living thing interacts with other organisms and its environment. One reason that biological systems can be difficult to study is that so many different interactions with other organisms and the environment are possible, even on the smallest of scales. A microscopic bacterium responding to a local sugar gradient is responding to its environment as much as a lion is responding to its environment when it searches for food in the African savannah. For any given species, behaviors can be co-operative, aggressive, parasitic or symbiotic. Matters become more complex when two or more different species interact in an ecosystem. Studies of this type are the province of ecology.
History
Although the concept of biology as a single coherent field arose in the 19th century, the biological sciences emerged from traditions of medicine and natural history reaching back to Galen and Aristotle in ancient Greece. During the Renaissance and early modern period, biological thought was revolutionized by a renewed interest in empiricism and the discovery of many novel organisms. Prominent in this movement were Vesalius and Harvey, who used experimentation and careful observation in physiology, and naturalists such as Linnaeus and Buffon who began to classify the diversity of life and the fossil record, as well as the development and behavior of organisms. Microscopy revealed the previously unknown world of microorganisms, laying the groundwork for cell theory. The growing importance of natural theology, partly a response to the rise of mechanical philosophy, encouraged the growth of natural history (though it entrenched the argument from design).[4]
Over the 18th and 19th centuries, biological sciences such as botany and zoology became increasingly professional scientific disciplines. Lavoisier and other physical scientists began to connect the animate and inanimate worlds through physics and chemistry. Explorer-naturalists such as Alexander von Humboldt investigated the interaction between organisms and their environment, and the ways this relationship depends on geography—laying the foundations for biogeography, ecology and ethology. Naturalists began to reject essentialism and consider the importance of extinction and the mutability of species. Cell theory provided a new perspective on the fundamental basis of life. These developments, as well as the results from embryology and paleontology, were synthesized in Charles Darwin's theory of evolution by natural selection. The end of the 19th century saw the fall of spontaneous generation and the rise of the germ theory of disease, though the mechanism of inheritance remained a mystery.[5]
In the early 20th century, the rediscovery of Mendel's work led to the rapid development of genetics by Thomas Hunt Morgan and his students, and by the 1930s the combination of population genetics and natural selection in the "neo-Darwinian synthesis". New disciplines developed rapidly, especially after Watson and Crick proposed the structure of DNA. Following the establishment of the Central Dogma and the cracking of the genetic code, biology was largely split between organismal biology—the fields that deal with whole organisms and groups of organisms—and the fields related to cellular and molecular biology. By the late 20th century, new fields like genomics and proteomics were reversing this trend, with organismal biologists using molecular techniques, and molecular and cell biologists investigating the interplay between genes and the environment, as well as the genetics of natural populations of organisms.[6]
See also
- Main lists: List of biology topics, List of basic biology topics and List of biologists
| Topics related to biology (Category) | |
|---|---|
| People and history | Biologist - Notable biologists - History of biology - Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine - Timeline of biology and organic chemistry - List of geneticists and biochemists |
| Institutions, publications | NASA Ames Research Center - Bachelor of Science - Publications |
| Terms and phrases | Omne vivum ex ovo - In vivo - In vitro - In utero - In silico |
| Related disciplines | Medicine (Physician) - Physical anthropology - Environmental science - Life Sciences - Biotechnology |
| Other | List of conservation topics |
References
- ^ Biology: A Functional Approach By Michael Bliss Vaughan Roberts. Cheltenham: Thomas Nelson and Sons, 1986. pg. 1
- ^ Dawkins, R. (1976) The Selfish Gene. Oxford University Press. Second edition (1989)
- ^ Woese C, Kandler O, Wheelis M (1990). "Towards a natural system of organisms: proposal for the domains Archaea, Bacteria, and Eucarya.". Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 87 (12): 4576-9. ISSN 0027-8424. PMID 2112744.
- ^ See: Mayr, The Growth of Biological Thought; Magner, A History of the Life Sciences
- ^ See: Bowler, Evolution; Coleman, Biology in the Nineteenth Century;, Mayr, The Growth of Biological Thought
- ^ See: Allen, Life Science in the Twentieth Century; Fruton, Proteins, Enzymes, Genes; Morange, A History of Molecular Biology; Smocovitis, Unifying Biology
Further reading
- Margulis, Lynn (1997). Five Kingdoms: An Illustrated Guide to the Phyla of Life on Earth, 3rd edition, St. Martin's Press. ISBN 0-8050-7252-7. (many other editions)
- Campbell, Neil (2004). Biology, 7th edition, Benjamin-Cummings Publishing Company. ISBN 0-8053-7146-X.
- Johnson, George B. (2005). Biology, Visualizing Life. Holt, Rinehart, and Winston. ISBN 0-03-016723-X.
External links
- The Dolan DNA Learning Center: The source for timely information about your life
- PhyloCode, http://www.ohiou.edu/phylocode/index.html
- The Tree of Life: A multi-authored, distributed Internet project containing information about phylogeny and biodiversity.
- MIT video lecture series on biology
- A wiki site for protocol sharing run from MIT.
- Biology online wiki dictionary.
- Biology News Net.
Journal links
- PLos Biology A peer-reviewed, open-access journal published by the Public Library of Science
- International Journal of Biological Sciences A biological journal publishes peer-reviewed scientific papers of significance
- Perspectives in Biology and Medicine